1) Conductor
The conductors shall be of Class 1 or 2 of plain or clad annealed copper or of plain aluminum or aluminum alloy or of Class 5 of plain or clad copper in accordance with IEC 60228.
Low voltage power and control cables IEC 60502-1 rated voltage 1/0.6 kV
Summary of IEC 60502-1 (2009)
Reference standard for low voltage cables (1/0.6 kV) and 3/1.8 kV

The conductors shall be of Class 1 or 2 of plain or clad annealed copper or of plain aluminum or aluminum alloy or of Class 5 of plain or clad copper in accordance with IEC 60228.

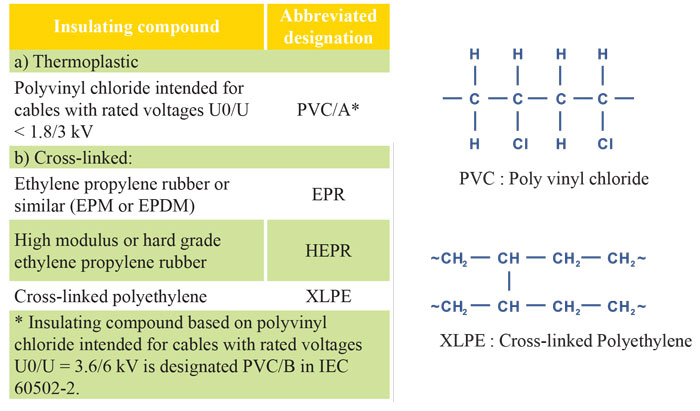
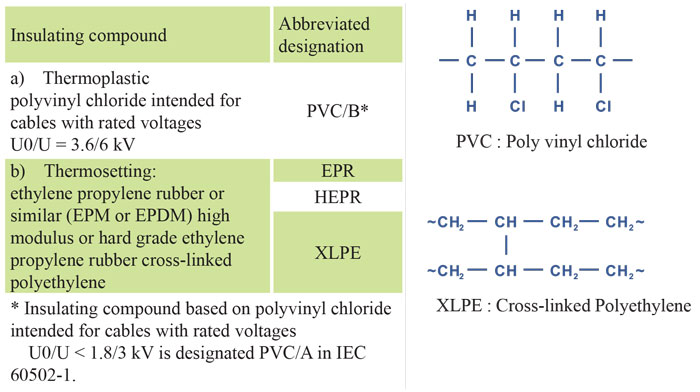
The insulation must be an extruded dielectric of one of the types listed in the table below.
For halogen-free cables, the insulation must meet the requirements given in the table: Halogen-free composition requirements. Insulation compounds The types of insulation compounds covered by this standard are listed in the table below. along with their abbreviations
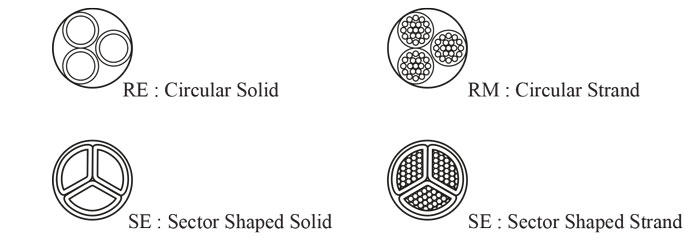
Construction:
Gaps in the concentric conductor must comply with national regulations and/or standards. requirements : Dimensional, physical and electrical requirements of sheet metal shall be determined by regulations and/or national standards.Concentric conductor cross section according to VDE 0271 (for NYCY and similar):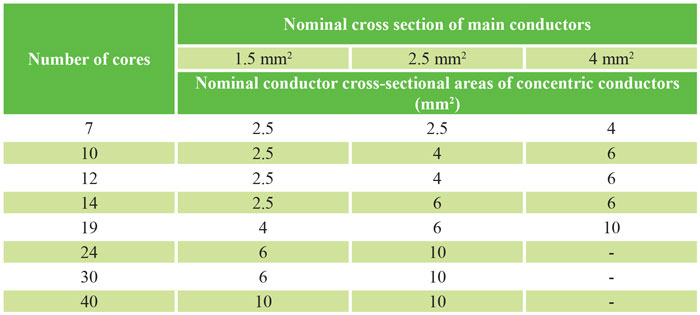
The sheath should consist of lead or lead alloy and should be used as a relatively strong seamless tube.
The lead sheath is used to protect the cables against the penetration of moisture and especially oil and chemicals in petrochemical factories and refineries.

Types of metal armor:
The types of armor covered by this standard are as follows:
A) flat wire armor
b) round wire armor
c) Double strip armor
Round or flat wires should be galvanized steel, copper or tinned copper, aluminum or aluminum alloy. Strips should be made of steel, galvanized steel, aluminum or aluminum alloy.
Steel strips shall be hot or cold rolled of commercial quality.
Braid armor can be used for cables with a conductor cross-section equal to or less than 6 mm2.
Armored single core cables for use in AC. Systems must be made of non-magnetic materials, unless a special construction is chosen.

General :
All cables must be sheathed.
The sheath is usually black, but a color other than black may be provided by agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser, provided it is suitable for the particular conditions under which the cable is used.
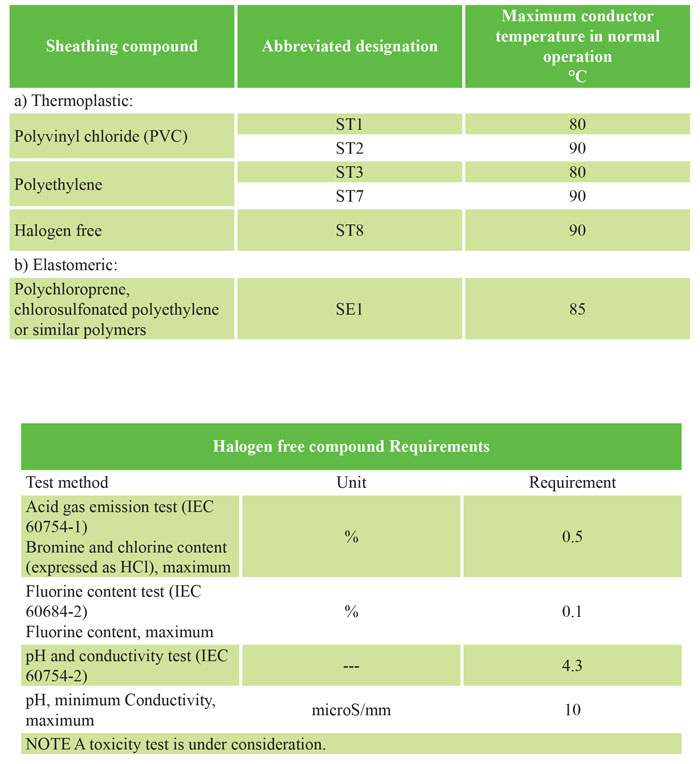
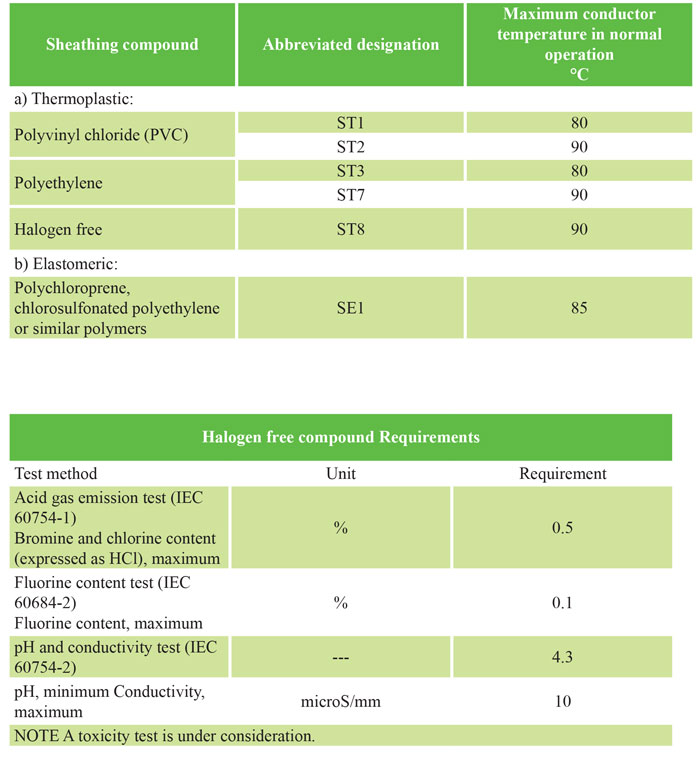
The coating must consist of a thermoplastic compound (PVC or polyethylene or halogen-free) or an elastomeric compound (polychloroprene, polyethylene chlorosulfone or similar polymers). Halogen-free sheathing materials should be used in cables that have flame retardant properties, low smoke emission levels, and halogen-free gas emissions when exposed to fire.
The sheath (ST8) of halogen-free cables shall meet the requirements given in the table entitled: Halogen-free composition requirements.
The coating material must be suitable for the operating temperature according to the table below.
Chemical additives may be requested for use in coatings for specific purposes, for example termite protection, but must not contain substances harmful to humans and/or the environment.
Note: Examples of materials that are considered undesirable include:
Aldrin 1,2,3,4,10,10-hexachloro-1,4,4a,5,8,8a-hexahydro-1,4,5,8-dimethanonaphthalene
Dieldrin 1,2,3,4,10,10-hexachloro-6,7-epoxy-1,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-1,4,5,8-dimethanonaphthalene
Lindane gamma isomer of 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane.
Coating compounds
The maximum conductive temperature for different types of coating composition covered by this standard is given in the table below.
Medium voltage cables IEC 60502-2 6/3.6 kV to 30/18 kV
A summary of the IEC 60502-2 (2005) standard
Reference for medium voltage cables 6.3.6 to 18.30 kV
Conductors shall be Class 1 or Class 2 of plain or clad annealed copper or of plain aluminum or aluminum alloy in accordance with IEC 60228.
For Class 2 conductors, measures may be taken to achieve longitudinal sealing

The insulation must be an extruded dielectric of one of the types listed in the table below.
Internal coatings may be extruded or laminated
The materials used for the inner coverings and fillers must be suitable for the operating temperature of the cable and compatible with the insulating material.
For halogen-free cables, the inner sheath and fillers must meet the requirements given in the table entitled: Halogen-free composition requirements. For cables having neither armour, concentric conductors nor other collective metal layers, the inner sheath may be omitted, provided that the outer sheath is present. The shape of the cable practically remains circular.
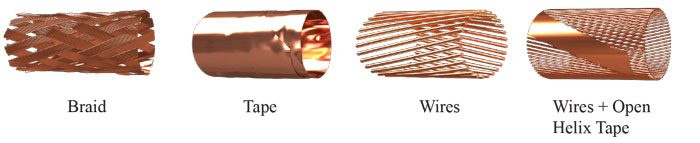
All cables must have a metal layer around the cores, individually or collectively.
Screening of single cores in single or three core cables, if required, should consist of a conductor plate and an insulating plate. At rated voltage 3.6/6 (7.2) kV PVC insulated cables should not be screened.
The conductor plate shall be non-metallic and consist of an extruded semi-conductive compound which may be applied to the semi-conductive strip.
The extruded semiconductor compound must be firmly bonded to the insulator.
The insulating plate must consist of a semi-conducting non-metallic layer in combination with a metallic layer. The non-metallic layer shall be extruded directly over the insulation of each core and shall consist of a bonded or separable semi-conductive compound.
A layer of semiconducting tape or compound may then be applied to individual cores or sets of cores. The metal layer shall be applied to each core or set of cores collectively and shall comply with the requirements of the following clause.
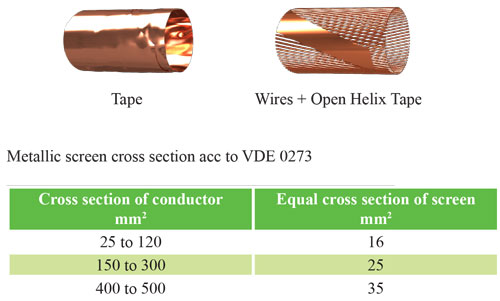
The metal plate must consist of one or more strips, or a braid, or a concentric layer of wire or a combination of wire and strip(s). Screen gaps must comply with national regulations and/or standards. Dimensional, physical and electrical requirements of sheet metal
It should be determined by regulations and/or national standard

Construction:
The metal plate must consist of one or more strips, or a braid, or a concentric layer of wire or a combination of wire and strip(s).
Requirements: Dimensional, physical and electrical requirements of sheet metal shall be determined by regulations and/or national standards.
The sheath should consist of lead or lead alloy and should be used as a relatively strong seamless tube.
The lead sheath is used to protect the cables against the penetration of moisture and especially oil and chemicals in petrochemical factories and refineries.

Types of metal armor:
The types of armor covered by this standard are as follows:
A) flat wire armor
b) round wire armor
c) Double strip armor
Round or flat wires should be galvanized steel, copper or tinned copper, aluminum or aluminum alloy.
Strips should be made of steel, galvanized steel, aluminum or aluminum alloy.
Steel strips shall be hot or cold rolled of commercial quality.
Armored single core cables for use in AC. Systems must be made of non-magnetic materials, unless a special construction is chosen.
General :
All cables must be sheathed.
The sheath is usually black, but a color other than black may be provided by agreement between the manufacturer and the purchaser, provided it is suitable for the particular conditions under which the cable is used.
The coating must consist of a thermoplastic compound (without PVC or polyethylene or halogen) or an elastomeric compound (polychloroprene, chlorosulfonated polyethylene or similar polymers). Halogen-free sheathing materials should be used in cables that have flame retardant properties and low levels. Smoke emissions and halogen-free gas emissions when exposed to fire.
The sheath (ST8) of halogen-free cables shall meet the requirements given in the table entitled: Halogen-free composition requirements.
The coating material must be suitable for the operating temperature according to the table below.
Chemical additives may be requested for use in coatings for specific purposes, for example termite protection, but must not contain substances harmful to humans and/or the environment.
Note: Examples of materials that are considered undesirable include:
Aldrin 1,2,3,4,10,10-hexachloro-1,4,4a,5,8,8a-hexahydro-1,4,5,8-dimethanonaphthalene
Dieldrin 1,2,3,4,10,10-hexachloro-6,7-epoxy-1,4,4a,5,6,7,8,8a-octahydro-1,4,5,8-dimethanonaphthalene
Lindane gamma isomer of 1,2,3,4,5,6-hexachlorocyclohexane.
Coating compounds
The maximum conductive temperature for different types of coating composition covered by this standard is given in the table below.